Selección de interfaz LCD para monitores y ordenadores industriales

Consideraciones de ingeniería más allá de la compatibilidad básica de señales En los proyectos de monitores y Panel PC industriales, la selección de la interfaz LCD ...
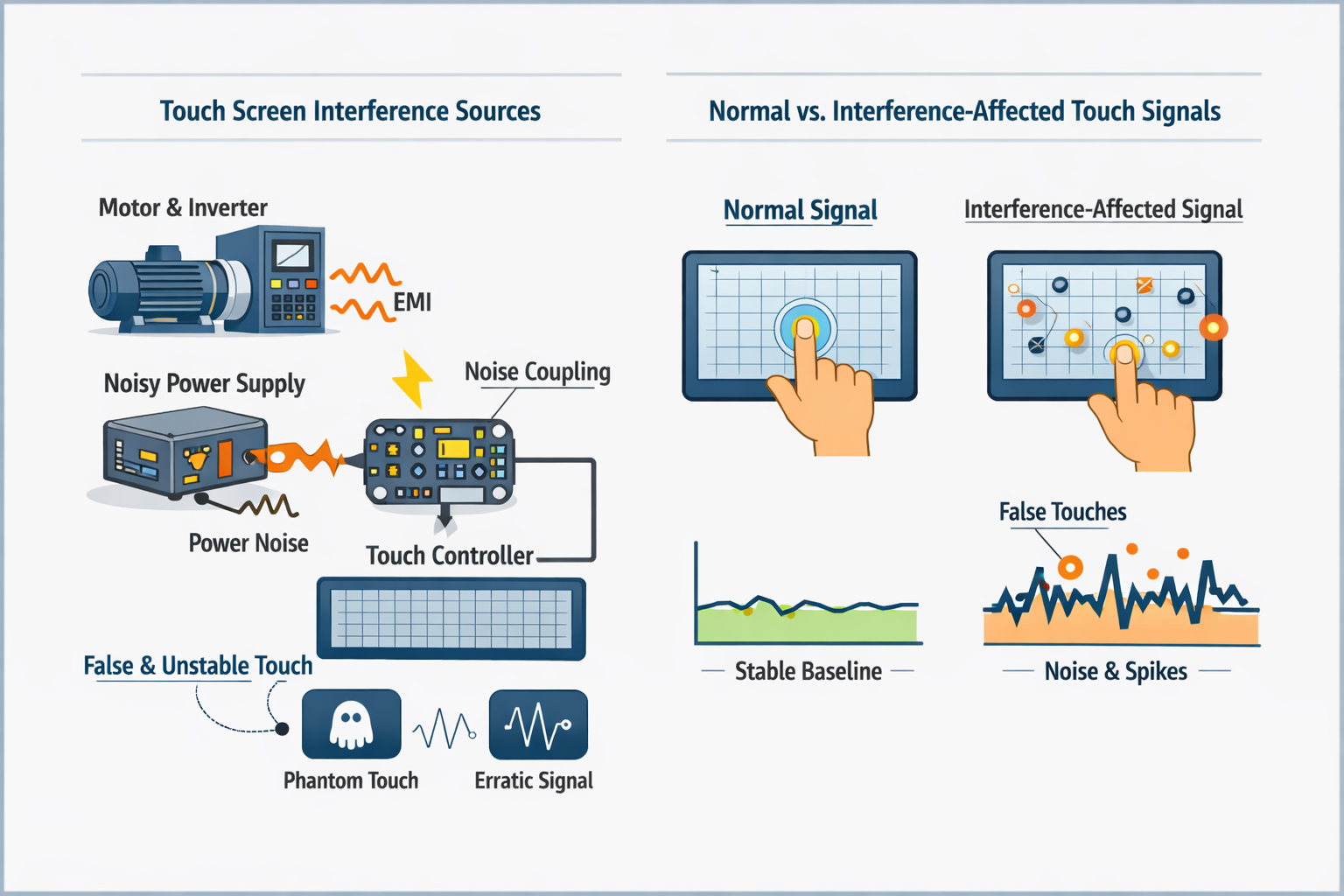
Touch screen interference refers to unwanted electrical noise that disrupts normal touch signal detection, leading to unstable or incorrect touch behavior.
In industrial capacitive touch systems, interference is not a software bug, but a system-level phenomenon related to electrical noise, grounding, power quality, and mechanical integration.
Common manifestations include false touch, drifting touch points, unstable coordinates, or intermittent loss of touch accuracy.
Interference-related issues often appear as:
These symptoms are frequently environment- or integration-dependent, not panel-only defects.
From an engineering perspective, touch interference usually originates from one or more of the following sources:
Touch interference is rarely caused by a single factor; it is typically the combined effect of multiple marginal conditions.
An interference evaluation is recommended when:
Early evaluation helps distinguish integration-related noise from controller or sensor limitations.
Touch interference is assessed by observing signal stability and noise behavior rather than relying on touch coordinates alone.
Typical evaluation methods include:
Tool-based diagnostics (e.g., controller tuning or raw data visualization) are often used by engineers, but interpretation of results is application-specific and should not rely on fixed numeric thresholds alone.
Interference mitigation should be addressed at the system design stage, not as a post-deployment workaround.
Key considerations include:
No single measure guarantees immunity; effective control comes from coordinated electrical and mechanical design.
In industrial projects, touch interference issues are most often traced back to system-level integration decisions, rather than the touch sensor alone.
Successful deployments typically evaluate touch performance together with display behavior, power design, enclosure grounding, and environmental EMI exposure—especially for HMI, kiosks, and unattended systems.
A technical review is recommended if your project involves:
Experiencing unstable or false touch behavior in your system?
Share your application environment, system architecture, and observed symptoms with our engineering team for an interference feasibility and risk review.
This page is intended as a technical reference for understanding and evaluating touch screen interference in industrial applications. Tool-specific diagnostic procedures may vary by controller platform and project.

Consideraciones de ingeniería más allá de la compatibilidad básica de señales En los proyectos de monitores y Panel PC industriales, la selección de la interfaz LCD ...

Por qué una mayor protección contra la penetración no siempre es sinónimo de mayor fiabilidad En los proyectos de Panel PC industriales, IP ...

1. Comprensión de los problemas de las pantallas táctiles capacitivas Las pantallas táctiles capacitivas se utilizan ampliamente en sistemas industriales y comerciales debido a ...
1. Comprensión de las pantallas táctiles “sin respuesta” Una pantalla táctil sin respuesta se refiere a una condición en la que la entrada táctil ...
Comparta su solicitud y los requisitos clave para Monitores táctiles o Paneles PC. Nuestros ingenieros revisarán la viabilidad, los riesgos y recomendarán la dirección de configuración adecuada.