Auswahl von LCD-Schnittstellen für industrielle Panel-PCs und Monitore

Technische Überlegungen, die über die grundlegende Signalkompatibilität hinausgehen Bei industriellen Panel-PC- und Monitorprojekten ist die Auswahl der LCD-Schnittstelle ...

Image retention, commonly referred to as ghosting, describes a condition where faint traces of previously displayed content remain visible after the image has changed.
In industrial TFT LCD applications, ghosting is typically not a product defect, but a display behavior resulting from the combined effect of panel characteristics, driving method, operating environment, and application usage pattern.
Understanding this distinction is critical when evaluating display suitability for long-term or mission-critical deployments.
From an engineering standpoint, image retention observed in TFT LCDs can originate from different mechanisms. Identifying the type helps determine whether the risk can be reduced through selection or integration decisions.
Temporary Image Retention
Driving or Bias-Related Retention
Long-Term Degradation Related Retention
Not all contributing factors are equally controllable. From a system design perspective, it is important to distinguish between design-controllable parameters and application-driven constraints.
| Factor | Engineering Control | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| LCD response time | High | Evaluated during panel selection |
| Driver board matching | High | Electrical compatibility is critical |
| Static UI ratio | Medium | Strongly tied to application design |
| Betriebstemperatur | Medium | System-level thermal management |
| Panel aging | Low | Inherent lifecycle behavior |
Ghosting risk is rarely attributable to a single parameter; it is usually the result of multiple marginal conditions stacking together.
Ghosting likelihood varies significantly depending on how the display is used in the field.
Understanding where an application falls within this spectrum is often more important than focusing on panel specifications alone.
Rather than relying on post-deployment mitigation, ghosting risk should be evaluated during the selection and integration phase.
Zu den wichtigsten Überlegungen gehören:
No TFT LCD can guarantee zero image retention under all conditions; the goal is risk control, not absolute elimination.
In industrial projects, image retention is most often observed when application behavior, electrical driving, and thermal conditions are evaluated independently rather than as a system.
During display selection and integration reviews, these factors are typically assessed together to determine long-term suitability and operational risk—especially for 24/7 HMI, kiosk, and unattended systems.
A technical review is recommended if your application involves:
Not sure if your application is suitable for long-term static display operation?
Share your operating conditions, UI behavior, and environment details with our engineering team for a feasibility and risk review.
This content is intended as an engineering reference for display behavior evaluation and should be considered in the context of complete system design.

Technische Überlegungen, die über die grundlegende Signalkompatibilität hinausgehen Bei industriellen Panel-PC- und Monitorprojekten ist die Auswahl der LCD-Schnittstelle ...

Warum ein höherer Schutz nicht immer eine höhere Zuverlässigkeit bedeutet Bei industriellen Panel-PC-Projekten bedeutet IP ...

1. Verständnis der Probleme mit kapazitiven Touchscreens Kapazitive Touchscreens sind in industriellen und kommerziellen Systemen weit verbreitet, da sie ...
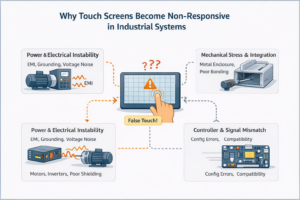
1. Verständnis von “nicht reagierenden” Touchscreens Ein nicht reagierender Touchscreen bezieht sich auf einen Zustand, bei dem die Berührungseingabe ...
Teilen Sie Ihre Bewerbung und die wichtigsten Anforderungen für Touch-Monitore oder Panel-PCs. Unsere Ingenieure prüfen die Machbarkeit, die Risiken und empfehlen die richtige Konfigurationsrichtung.