산업용 패널 PC 및 모니터를 위한 LCD 인터페이스 선택

기본적인 신호 호환성 그 이상의 엔지니어링 고려 사항 산업용 패널 PC 및 모니터 프로젝트에서 LCD 인터페이스 선택 ...

In industrial automation, embedded computing plays a critical role in real-time control, data acquisition, edge intelligence, and machine-level communication. Among the various architectures available, fanless embedded computers are increasingly preferred because they deliver higher operational reliability, improved uptime, reduced maintenance, and long product lifecycles—especially in harsh environments where dust, vibration, and temperature swings are common.
A fanless embedded computer is a ruggedized computing system engineered for continuous operation without traditional cooling fans. Instead of active airflow, these systems rely on passive thermal design, such as large surface heatsinks, optimized chassis materials, and efficient heat conduction, to dissipate system heat while remaining sealed against contaminants.
Unlike desktop PCs with fans that pull ambient air through the chassis, fanless embedded computers use advanced passive cooling to maintain safe operating temperatures even under constant workloads.
Traditional fans are among the most failure-prone components in industrial computers due to moving parts and susceptibility to dust. By eliminating fan assemblies, fanless embedded computers significantly reduce mechanical failures. This increases Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) and reduces unscheduled downtime—critical for systems that must run 24/7.
This component-level simplification translates into fewer service interventions and lower operating risk—especially in dusty factory floors, food processing plants, and outdoor gateways.
Fanless designs do not require airflow through the system, which means they can be completely sealed. This prevents dust, debris, and contaminants from entering sensitive circuitry—an important advantage where traditional fan-cooled systems rapidly accumulate particles that degrade performance and reliability.
Sealed fanless enclosures are especially valuable in vibration-intense settings such as automotive assembly lines, heavy machinery rooms, and logistic hubs.
The absence of fans results in near-silent operation, eliminating the noise associated with traditional cooling systems. For industrial environments where acoustic disturbance is a concern—such as laboratories, control rooms, or offices—fanless systems contribute to a quieter operational environment.
Without fan filters or air paths to clean, ongoing maintenance becomes simpler and less frequent.
Fanless embedded computers often incorporate low-power embedded CPUs which generate less heat and require less cooling energy. This translates into:
Energy-efficient operation aligns with modern businesses’ sustainability goals and lowers total cost of ownership over long lifecycles.
Fanless embedded computers are purpose-built for environments where reliability and longevity are non-negotiable:
Their sealed architecture and passive cooling make them ideal for applications where dust resistance, temperature flexibility, and maintenance-free operation are required.
Fanless systems rely primarily on passive cooling mechanisms, such as:
By using efficient thermal conduction and chassis design, fanless embedded computers maintain safe internal temperatures without drawing air through the chassis. This prevents dust ingress, improves longevity, and increases operational stability in challenging environments.
Choosing the right fanless embedded computer requires a holistic assessment of project requirements:
Select processors and architectures that match the application:
Ensure the system supports required temperature ranges and vibration tolerances. Fanless systems often perform reliably in extended temperature ranges from -20°C to 70°C or beyond, depending on design.
Evaluate I/O requirements such as serial ports (RS-232/RS-485), multiple LAN interfaces, USB, and specialized industrial interfaces. This ensures seamless integration with sensors, actuators, and industrial buses.
Industrial deployments often last many years. Confirm that the supplier can provide support, firmware updates, and replacement parts. Certification to relevant industry standards also improves trust.
Factor in maintenance costs, energy consumption, and lifecycle expectancy. Fanless designs typically deliver lower total operational cost due to higher uptime and reduced maintenance.
Fanless embedded computers are a robust and efficient computing solution for modern industrial and edge computing applications. By eliminating moving parts and relying on passive cooling, they deliver higher reliability, lower maintenance, silent performance, and energy efficiency. For businesses seeking dependable 24/7 systems that thrive in dusty, vibration-intense, or temperature-challenging environments, fanless embedded computing is often the preferred choice.
When evaluating fanless systems, buyers should consider performance needs, environmental conditions, and long-term support to ensure the optimal selection. A well-chosen fanless embedded computer not only improves system uptime but also reduces total cost of ownership and supports future growth.

기본적인 신호 호환성 그 이상의 엔지니어링 고려 사항 산업용 패널 PC 및 모니터 프로젝트에서 LCD 인터페이스 선택 ...

더 높은 침입 보호가 항상 더 높은 안정성을 의미하지는 않는 이유 산업용 패널 PC 프로젝트에서, IP ...

1. 정전식 터치스크린 문제 이해 정전식 터치스크린은 다음과 같은 이유로 산업 및 상업용 시스템에서 널리 사용됩니다. ...
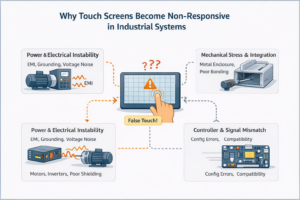
1. “비응답” 터치 스크린 이해 비응답 터치 스크린이란 터치 입력이 제대로 되지 않는 상태를 말합니다. ...
애플리케이션 및 주요 요구 사항 공유 터치 모니터 또는 패널 PC. 엔지니어가 타당성과 위험성을 검토하고 올바른 구성 방향을 추천해 드립니다.