산업용 패널 PC 및 모니터를 위한 LCD 인터페이스 선택

기본적인 신호 호환성 그 이상의 엔지니어링 고려 사항 산업용 패널 PC 및 모니터 프로젝트에서 LCD 인터페이스 선택 ...

In industrial deployments, display failures rarely occur suddenly.
Most failures are the result of long-term thermal stress, accumulated quietly over months or years of operation.
For industrial-grade displays operating 24/7, inside sealed enclosures, or under elevated ambient temperatures, thermal management is not a secondary design consideration — it is the primary determinant of service life.
This reference explains how heat is generated inside industrial displays, how it accelerates aging, and what thermal design decisions directly affect lifespan.
Industrial displays differ fundamentally from consumer displays in how they are used:
Under these conditions, internal temperature rise is unavoidable.
What matters is whether the system is designed to control, spread, and dissipate that heat predictably over time.
Thermal stress rarely causes immediate failure.
Instead, it accelerates material aging, electronic drift, and gradual performance degradation.
Understanding lifespan begins with understanding where heat originates.
In most industrial displays, the backlight assembly generates the largest share of internal heat.
Backlight temperature is strongly correlated with:
Power supplies and voltage regulators operate continuously and generate localized heat.
Over time, elevated temperature in these areas contributes to:
These effects often appear late in the deployment cycle, making root-cause diagnosis difficult.
Timing controllers, interface chips, and signal processing circuits generate concentrated thermal hotspots.
Without proper heat spreading, these localized zones can:
Thermal stress affects multiple failure mechanisms simultaneously.
Sustained high temperature:
Even displays specified for high brightness can experience rapid degradation if thermal margins are insufficient.
Elevated temperature accelerates:
Repeated heating and cooling cycles further compound mechanical fatigue.
In touch-enabled displays, thermal stress may affect:
These issues often emerge gradually and are difficult to correct after deployment.
Thermal behavior must always be evaluated in real deployment environments.
Displays installed in sealed cabinets or kiosks experience:
Without defined thermal paths, heat has no effective escape route.
Solar loading can raise enclosure temperature far above ambient air temperature.
Even displays rated for high operating temperatures may suffer accelerated aging without proper solar and thermal mitigation.
Fanless designs eliminate mechanical wear but rely entirely on:
In these systems, thermal margin becomes a hard design constraint.
In industrial display design, temperature is not just an environmental parameter.
It is a lifecycle variable that directly influences:
Many premature display failures attributed to “quality issues” are, in reality, the result of insufficient thermal planning at system level.
Thermal considerations must be addressed before enclosure and mounting designs are finalized.
Early thermal review helps identify:
Addressing thermal behavior early prevents:
Note
Display lifespan is not defined by specification alone.
It is defined by how temperature is managed throughout real-world deployment.

기본적인 신호 호환성 그 이상의 엔지니어링 고려 사항 산업용 패널 PC 및 모니터 프로젝트에서 LCD 인터페이스 선택 ...

더 높은 침입 보호가 항상 더 높은 안정성을 의미하지는 않는 이유 산업용 패널 PC 프로젝트에서, IP ...

1. 정전식 터치스크린 문제 이해 정전식 터치스크린은 다음과 같은 이유로 산업 및 상업용 시스템에서 널리 사용됩니다. ...
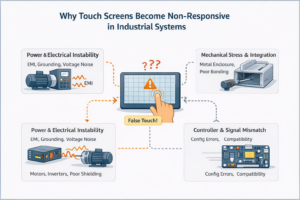
1. “비응답” 터치 스크린 이해 비응답 터치 스크린이란 터치 입력이 제대로 되지 않는 상태를 말합니다. ...
애플리케이션 및 주요 요구 사항 공유 터치 모니터 또는 패널 PC. 엔지니어가 타당성과 위험성을 검토하고 올바른 구성 방향을 추천해 드립니다.