اختيار واجهة LCD لأجهزة الكمبيوتر الشخصية والشاشات ذات اللوحات الصناعية

اعتبارات هندسية تتجاوز توافق الإشارات الأساسية في مشاريع الحواسيب الشخصية والشاشات ذات اللوحات الصناعية، اختيار واجهة LCD ...

Embedded computing systems and embedded PCs are foundational technologies in modern industrial automation, smart manufacturing, edge computing, and connected equipment. Unlike general-purpose desktops or servers, these systems are purpose-built for continuous, reliable, task-specific operation in demanding environments.
In this guide, we explain what embedded computing systems are, why they matter in industrial applications, and how to choose the right embedded PC for your specific needs.
أن embedded computing system refers to a dedicated computing architecture designed to perform specific control, processing, or monitoring tasks within a larger system or device.
Embedded computing systems are widely used in industrial automation, smart machinery, robotics, IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things), digital signage, and edge AI processing.
أن embedded PC is a type of embedded computing system that integrates the core architecture of a PC in a purpose-built, industrial form factor.
Different from consumer PCs, embedded PCs are designed for reliability, compact size, and long lifecycles. They are commonly deployed in:
Embedded PCs often feature rugged enclosures, fanless cooling, and industrial-grade components that operate reliably in environments with vibration, dust, temperature extremes, and EMI (electromagnetic interference).
| Aspect | Embedded PC | Consumer PC |
|---|---|---|
| Design Purpose | Specific industrial tasks | General computing |
| Operating Environment | Extreme temperature, vibration, dust | Controlled indoor |
| Reliability | High, 24/7 uptime | Limited by consumer use |
| Longevity | Long lifecycle support | Short upgrade cycles |
| Expandability | Industrial I/O, custom interfaces | Standard peripherals |
While consumer PCs focus on versatility and user experience, embedded PCs are purpose-built for reliable duty in industry-grade scenarios without frequent hardware changes.
Embedded computing systems are engineered to run 24/7 in harsh conditions without failure — a requirement in industrial automation and manufacturing.
Many embedded PCs use fanless designs and sealed units to prevent dust, moisture, and particulate ingress, significantly increasing reliability in factory floors and outdoor installations.
Embedded systems are optimized for specific workloads with efficient power usage, lower latency, and predictable performance — ideal for real-time control, IIoT gateways, and edge processing.
Industrial deployments often require hardware availability for years or even decades. Embedded PCs typically offer lifecycle stability and long-term availability, reducing requalification and redesign efforts.
From cold-storage facilities to high-temperature production lines, embedded computing hardware is built to handle environments where consumer devices would fail.
Embedded PCs are found in nearly every sector where reliable, specific task computing is required:
These systems bridge the gap between raw sensor data and actionable analytics, often serving at the edge where low latency and high reliability are key drivers.
Selecting an embedded PC is not one-size-fits-all. The ideal choice depends on your application requirements.
Consider CPU performance, memory, and storage based on the workload — from basic control logic to complex AI inference.
Check operating temperature range, vibration tolerance, and ingress protection ratings relevant to your deployment.
Ensure necessary industrial interfaces (e.g., serial COM, USB, Ethernet, CAN, GPIO) and expansion options are available.
Fanless and compact designs are preferred in dusty or vibration-heavy environments. Rack-mount or panel mount may be needed in others.
Industrial systems may need 24V DC or wide-range power inputs, remote power control, or ignition sensing.
Choose platforms compatible with your software stack — Windows, Linux, or real-time OS depending on use case.
These factors help you match the embedded PC to your business needs and operational environment.
Each form factor balances performance, durability, and integration flexibility for specific industrial requirements.
Embedded computing systems and embedded PCs are not just components — they are core enablers of modern industrial digitalisation, automation, and edge intelligence. Their reliability, tailored performance, and adaptability to harsh environments make them indispensable in today’s industrial applications.
Choosing the right embedded PC requires a deep understanding of your operational environment, performance needs, and integration constraints. When selected correctly, embedded computing systems deliver long-term stability, efficient operation, and significant ROI for industrial enterprises.

اعتبارات هندسية تتجاوز توافق الإشارات الأساسية في مشاريع الحواسيب الشخصية والشاشات ذات اللوحات الصناعية، اختيار واجهة LCD ...

لماذا لا تعني الحماية العالية من الدخول لا تعني دائمًا موثوقية أعلى في مشاريع الحواسيب الشخصية للوحات الصناعية ...

1. فهم مشاكل شاشات اللمس السعوية تستخدم شاشات اللمس السعوية على نطاق واسع في الأنظمة الصناعية والتجارية بسبب ...
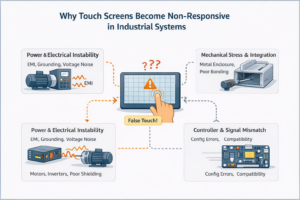
1. فهم الشاشات اللمسية “غير المستجيبة” تشير شاشة اللمس غير المستجيبة إلى حالة يكون فيها الإدخال باللمس ...
شارك طلبك ومتطلباتك الرئيسية لـ الشاشات التي تعمل باللمس أو لوحة أجهزة الكمبيوتر الشخصية. سوف يقوم مهندسونا بمراجعة الجدوى والمخاطر والتوصية باتجاه التكوين الصحيح.