산업용 패널 PC 및 모니터를 위한 LCD 인터페이스 선택

기본적인 신호 호환성 그 이상의 엔지니어링 고려 사항 산업용 패널 PC 및 모니터 프로젝트에서 LCD 인터페이스 선택 ...
Energy efficiency is increasingly important in industrial systems — especially in 24/7 operation, outdoor deployments, and unattended equipment.
As a result, features such as automatic dimming 그리고 power-saving modes are frequently requested in industrial display specifications.
However, in industrial environments, any automatic behavior must be treated as a system-level decision, not just a feature checkbox.
This reference explains how automatic dimming and power management work in industrial displays, where they deliver real value, and where they may introduce operational risk.
Industrial displays often operate under conditions very different from consumer electronics:
In these scenarios, unmanaged display brightness can become a major contributor to:
Power control mechanisms exist to address these challenges — but only when properly integrated at system level.
Automatic dimming typically relies on an ambient light sensor that adjusts backlight brightness based on surrounding light conditions.
In industrial implementations, this mechanism usually includes:
When engineered correctly, automatic dimming can:
The key issue is not whether dimming exists, but how it behaves when conditions change or sensors fail.
In industrial systems, automatic brightness adjustment is not always desirable.
In control or safety-related interfaces, unexpected brightness changes may:
For safety-critical HMIs, fixed and validated brightness levels are often preferred.
Automatic dimming depends on sensor input.
If the sensor is:
The display may respond incorrectly.
Industrial designs must define:
In environments with rapidly changing light conditions — such as:
Frequent brightness changes can reduce usability rather than improve it.
Power management in industrial displays goes beyond dimming.
Typical power-saving mechanisms include:
These modes can significantly reduce energy consumption, but they must be coordinated with:
A display that enters power-saving mode too aggressively may appear unresponsive in time-critical operations.
These features are generally well-suited for:
In these cases, energy efficiency and component longevity outweigh constant visual consistency.
Automatic dimming and aggressive power-saving may not be appropriate for:
In such deployments, predictable behavior is often more important than energy optimization.
In industrial display design, power management is not a standalone feature.
It must be evaluated together with:
Many industrial projects enable dimming hardware support but limit or condition its use in software, ensuring predictable system behavior.
This approach balances efficiency with reliability.
If your system includes defined power budgets, outdoor exposure, or unattended operation, brightness and power behavior should be reviewed early in system design.
An engineering review can help determine:
Early decisions prevent late-stage usability and validation issues.
Note
This reference focuses on system behavior and integration considerations.
Power-saving features should always be evaluated within the context of the complete industrial system.

기본적인 신호 호환성 그 이상의 엔지니어링 고려 사항 산업용 패널 PC 및 모니터 프로젝트에서 LCD 인터페이스 선택 ...

더 높은 침입 보호가 항상 더 높은 안정성을 의미하지는 않는 이유 산업용 패널 PC 프로젝트에서, IP ...

1. 정전식 터치스크린 문제 이해 정전식 터치스크린은 다음과 같은 이유로 산업 및 상업용 시스템에서 널리 사용됩니다. ...
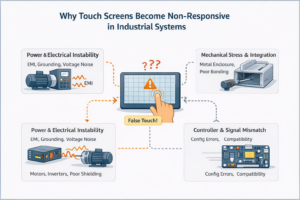
1. “비응답” 터치 스크린 이해 비응답 터치 스크린이란 터치 입력이 제대로 되지 않는 상태를 말합니다. ...
애플리케이션 및 주요 요구 사항 공유 터치 모니터 또는 패널 PC. 엔지니어가 타당성과 위험성을 검토하고 올바른 구성 방향을 추천해 드립니다.