産業用パネルPCとモニターにおけるLCDインターフェースの選択

基本的な信号互換性を超えたエンジニアリングの考慮事項 産業用パネルPCおよびモニタープロジェクトでは、LCDインターフェースの選択が重要です。 ...
In modern industrial and commercial display projects, glass surface treatment plays a critical role in readability, durability, and long-term usability.
Among the most commonly used solutions are AG (Anti-Glare), AF (Anti-Fingerprint), and AR (Anti-Reflective) glass treatments. Although they are often mentioned together, each serves a different technical purpose and application scenario.
This article explains the differences between AG, AF, and AR glass, how each treatment works, and how to select the right option for industrial displays in 2026.

AG glass, also known as anti-glare glass, is designed to reduce surface reflection by diffusing incoming light. This is typically achieved through chemical etching or micro-texturing of the glass surface.
Instead of reflecting light directly like a mirror, AG glass scatters light in multiple directions, significantly reducing glare caused by sunlight or strong artificial lighting.
AG glass is widely used in outdoor and semi-outdoor industrial displays, where sunlight readability is more important than perfect image clarity.

AF glass, or anti-fingerprint glass, is coated with an oleophobic layer that repels oils, moisture, and dirt. The primary purpose of AF treatment is not glare reduction, but surface cleanliness and ease of maintenance.
AF coatings reduce fingerprint visibility and allow smudges to be removed more easily, keeping the display surface clean even in high-touch environments.
AF glass is especially valuable in public or unattended systems, where frequent user interaction would otherwise lead to poor visual appearance and higher maintenance costs.
AF glass is commonly combined with AG or AR, rather than used alone.

AR glass, or anti-reflective glass, uses multi-layer optical coatings to minimize surface reflection by controlling light interference. Unlike AG glass, AR glass reduces reflection without diffusing light, preserving image sharpness and contrast.
High-quality AR coatings can reduce reflectance to below 1–2%, making the display appear clearer and more vivid even under strong ambient lighting.
AR glass is often used in high-brightness or premium display systems, especially when optical performance is a top priority.
| 特徴 | AG Glass | AF Glass | AR Glass |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glare Reduction | 高い | 低い | Very High |
| Fingerprint Resistance | 低い | Very High | ミディアム |
| Image Sharpness | ミディアム | 高い | Very High |
| Outdoor Suitability | 高い | ミディアム | Very High |
| Cost Level | 低い | Low–Medium | 高い |
Each treatment addresses a different technical problem, and none of them should be considered a universal solution.
Yes. In modern industrial display projects, combination treatments are increasingly common.
When combining treatments, coating compatibility and durability must be carefully engineered to avoid optical conflicts or reduced lifespan.
Selecting the correct glass treatment depends on application environment and usage conditions, not just specifications.
AG, AF, and AR glass treatments each serve a distinct purpose in industrial display design.
Understanding their differences helps engineers and procurement teams make informed decisions that improve readability, durability, and long-term performance.
Rather than choosing a glass treatment in isolation, it should be evaluated together with display brightness, touch technology, optical bonding, and environmental conditions to achieve the best overall system performance.

基本的な信号互換性を超えたエンジニアリングの考慮事項 産業用パネルPCおよびモニタープロジェクトでは、LCDインターフェースの選択が重要です。 ...

産業用パネルPCプロジェクトにおいて、IP保護等級が高くても信頼性が高いとは限らない理由 ...

1.静電容量式タッチスクリーンの問題を理解する 静電容量式タッチスクリーンは、以下の理由により産業用および商業用システムで広く使用されている。 ...
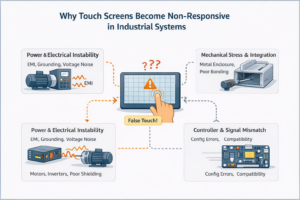
1.非反応型」タッチスクリーンを理解する 非反応型タッチスクリーンとは、タッチ入力が「非反応型」であることを意味します。 ...
あなたのアプリケーションと主な要件を共有する タッチモニター または パネルPC. 当社のエンジニアは、実現可能性、リスクを検討し、適切な構成の方向性を提案します。.