산업용 패널 PC 및 모니터를 위한 LCD 인터페이스 선택

기본적인 신호 호환성 그 이상의 엔지니어링 고려 사항 산업용 패널 PC 및 모니터 프로젝트에서 LCD 인터페이스 선택 ...
In modern industrial and commercial display projects, glass surface treatment plays a critical role in readability, durability, and long-term usability.
Among the most commonly used solutions are AG (Anti-Glare), AF (Anti-Fingerprint), and AR (Anti-Reflective) glass treatments. Although they are often mentioned together, each serves a different technical purpose and application scenario.
This article explains the differences between AG, AF, and AR glass, how each treatment works, and how to select the right option for industrial displays in 2026.

AG glass, also known as anti-glare glass, is designed to reduce surface reflection by diffusing incoming light. This is typically achieved through chemical etching or micro-texturing of the glass surface.
Instead of reflecting light directly like a mirror, AG glass scatters light in multiple directions, significantly reducing glare caused by sunlight or strong artificial lighting.
AG glass is widely used in outdoor and semi-outdoor industrial displays, where sunlight readability is more important than perfect image clarity.

AF glass, or anti-fingerprint glass, is coated with an oleophobic layer that repels oils, moisture, and dirt. The primary purpose of AF treatment is not glare reduction, but surface cleanliness and ease of maintenance.
AF coatings reduce fingerprint visibility and allow smudges to be removed more easily, keeping the display surface clean even in high-touch environments.
AF glass is especially valuable in public or unattended systems, where frequent user interaction would otherwise lead to poor visual appearance and higher maintenance costs.
AF glass is commonly combined with AG or AR, rather than used alone.

AR glass, or anti-reflective glass, uses multi-layer optical coatings to minimize surface reflection by controlling light interference. Unlike AG glass, AR glass reduces reflection without diffusing light, preserving image sharpness and contrast.
High-quality AR coatings can reduce reflectance to below 1–2%, making the display appear clearer and more vivid even under strong ambient lighting.
AR glass is often used in high-brightness or premium display systems, especially when optical performance is a top priority.
| 기능 | AG Glass | AF Glass | AR Glass |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glare Reduction | 높음 | Low | Very High |
| Fingerprint Resistance | Low | Very High | Medium |
| Image Sharpness | Medium | 높음 | Very High |
| Outdoor Suitability | 높음 | Medium | Very High |
| Cost Level | Low | Low–Medium | 높음 |
Each treatment addresses a different technical problem, and none of them should be considered a universal solution.
Yes. In modern industrial display projects, combination treatments are increasingly common.
When combining treatments, coating compatibility and durability must be carefully engineered to avoid optical conflicts or reduced lifespan.
Selecting the correct glass treatment depends on application environment and usage conditions, not just specifications.
AG, AF, and AR glass treatments each serve a distinct purpose in industrial display design.
Understanding their differences helps engineers and procurement teams make informed decisions that improve readability, durability, and long-term performance.
Rather than choosing a glass treatment in isolation, it should be evaluated together with display brightness, touch technology, optical bonding, and environmental conditions to achieve the best overall system performance.

기본적인 신호 호환성 그 이상의 엔지니어링 고려 사항 산업용 패널 PC 및 모니터 프로젝트에서 LCD 인터페이스 선택 ...

더 높은 침입 보호가 항상 더 높은 안정성을 의미하지는 않는 이유 산업용 패널 PC 프로젝트에서, IP ...

1. 정전식 터치스크린 문제 이해 정전식 터치스크린은 다음과 같은 이유로 산업 및 상업용 시스템에서 널리 사용됩니다. ...
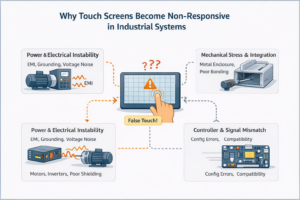
1. “비응답” 터치 스크린 이해 비응답 터치 스크린이란 터치 입력이 제대로 되지 않는 상태를 말합니다. ...
애플리케이션 및 주요 요구 사항 공유 터치 모니터 또는 패널 PC. 엔지니어가 타당성과 위험성을 검토하고 올바른 구성 방향을 추천해 드립니다.